The mutated gene does not cause any neurological or behavioral disorders.
The color patterns of the corn snake (Pantherophis guttatus), which can include reds, yellows, pinks, browns and more, are determined by a single gene called CLCN2, according to researchers with the University of Geneva.
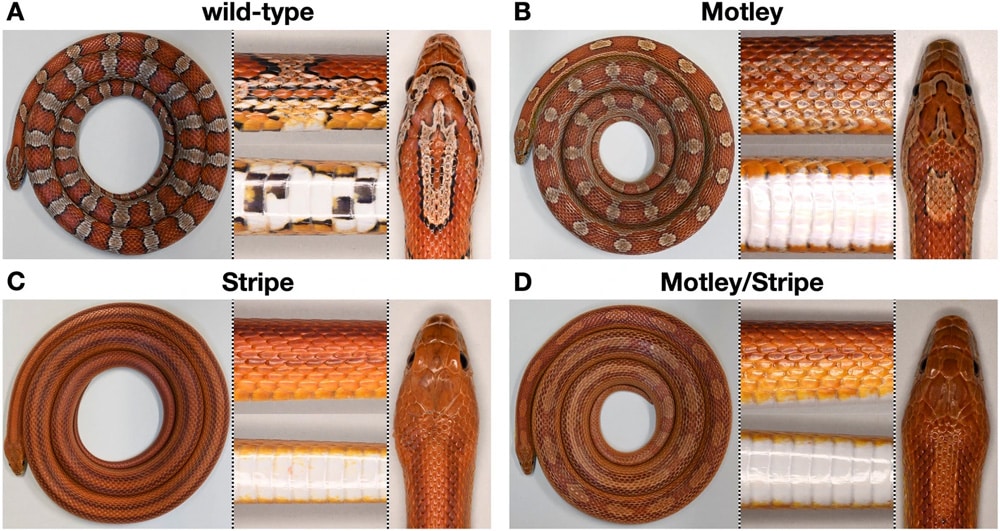
A typical wild corn snake has red blotches that are outlined in black on an orange background. The belly is usually black and white checkered in coloration. Corn snake morphs, however, exhibit a wide variety of colorations and patterns, some with black and white checkered bellies, and others, like the motley morph and the striped morph, lack the checkered patterns on their bellies.
Researchers Hatch Out First Gene-Edited Corn Snake Using CRISPR-Cas9
Researchers Athanasia Tzika, a senior lecturer at the University of Geneva, and Prof. Michel Milinkovitch of the Genetics and Evolution at UNIGE’s Faculty of Science, set out to find what causes these mutations.
The motley and striped snakes were crossed, and the researchers sequenced the genomes of the offspring. They determined that both phenotypes were linked to the mutations by the CLCN2 gene.
According to the researchers, the gene encodes a protein at the cell membrane. This creates a channel in which the chloride ions are transported across the membrane. The differential distribution of ions, the researchers say, creates an “electrical potential between the inside and outside of the cell.” This enables the transmission of cellular signals.
In the Motley snakes, the change is due to a strong reduction in its expression level. With the striped snakes, a small piece of DNA is inserted into the CLCN2 gene, which makes the protein non-functional. And there are no negative side effects to the snakes, which can reveal themselves in humans and in mice.
“These results were quite surprising, because in humans and mice, the CLCN2 channel is essential for neuronal activity, and mutations in this gene are associated with serious conditions such as leukoencephalopathy, a disease affecting the brain’s white matter,” say Sophie Montandon and Pierre Beaudier, researchers in the Milinkovitch/Tzika lab. They are also co-authors to the study.
“Our results show that a mutation in the CLCN2 gene in corn snakes does not cause neurological or behavioral disorders. However, the protein plays an essential, and previously unknown, role in the development of skin coloration patterns,” concludes Asier Ullate-Agote, co-first author of the study.
The complete paper, “Regulatory and disruptive variants in the CLCN2 gene are associated with modified skin color pattern phenotypes in the corn snake” can be read on the SpringerNature Link website.
Corn Snake Information
Corn snakes are probably the most popular snake kept for those new to reptile keeping. They are very easy to care for, have a very inquisitive disposition and come in a variety of morphs. They are native to the United States and are a species of North American rat snake. They grow to about 3-5 feet in length and can live more than 20 years.